- Vital signs – Measurements of a patient’s body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration rate.
- Patient assessment – A comprehensive evaluation of a patient’s physical and mental health.
- Medication administration – The process of giving medications to patients according to their prescribed dose and schedule.
- Patient education – Providing patients with information on how to manage their condition and maintain their health.
- Wound care – The management and treatment of wounds to promote healing and prevent infection.
- Intravenous therapy – The administration of medications and fluids directly into a patient’s bloodstream.
- Respiratory therapy – The treatment and management of respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia.
- Health promotion – Activities and interventions aimed at improving and maintaining a patient’s overall health.
- Pain management – The treatment and management of pain through medications, therapies, and other interventions.
- Nutrition management – The assessment and management of a patient’s nutritional needs and requirements.
- Infection control – Preventing and managing the spread of infectious diseases in healthcare settings.
- Care plan – A detailed plan of care for a patient that outlines their treatment and management goals.
- Patient safety – Ensuring the safety and well-being of patients through measures such as fall prevention and infection control.
- Medical history – A record of a patient’s past and current medical conditions, treatments, and medications.
- Nursing diagnosis – A clinical judgment made by a nurse about a patient’s health status and response to treatment.
- Patient advocacy – Supporting and advocating for patients to ensure they receive quality care and treatment.
- Geriatric care – Specialized care and treatment for elderly patients.
- Rehabilitation therapy – The management and treatment of conditions that affect mobility, strength, and function.
- Care coordination – Coordinating and integrating care across different healthcare providers and settings.
- Clinical documentation – Recording and documenting a patient’s medical history, treatment, and progress.
- Patient-centered care – Care that is focused on meeting the individual needs and preferences of each patient.
- Family education – Providing education and support to a patient’s family or caregiver.
- Discharge planning – Planning and coordinating a patient’s transition from the hospital or healthcare facility to home or another setting.
- Patient monitoring – Continuously monitoring a patient’s condition and response to treatment.
- Chronic disease management – The management and treatment of chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and COPD.
- Palliative care – Care and support for patients with serious illnesses and conditions to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Cardiac care – Specialized care and treatment for patients with heart conditions.
- Surgical care – Pre-operative and post-operative care for patients undergoing surgical procedures.
- Emergency care – Rapid assessment and treatment of patients with acute conditions and injuries.
- Obstetric care – Prenatal and postpartum care for pregnant women.
- Neonatal care – Specialized care and treatment for newborns and premature infants.
- Pediatric care – Specialized care and treatment for children.
- Oncology care – Care and treatment for patients with cancer.
- Hospice care – End-of-life care and support for patients with terminal illnesses.
- Rehabilitation nursing – Nursing care and support for patients undergoing rehabilitation therapy.
- Mental health nursing – Nursing care and support for patients with mental health conditions.
- Community health nursing – Nursing care and support for patients in the community.
- Home health nursing – Nursing care and support for patients in their home.
- Pain assessment – Evaluating and assessing a patient’s level of pain.
- Oxygen therapy – The administration of supplemental oxygen to patients who are experiencing difficulty breathing or have low oxygen levels.
- Assisted living – Providing care and support for patients who require assistance with daily activities.
- Inpatient care – Care and treatment provided to patients who require hospitalization.
- Outpatient care – Care and treatment provided to patients who do not require hospitalization.
- Patient satisfaction – Ensuring patients are satisfied with their care and treatment experience.
- Ethics in nursing – Upholding ethical principles and values in nursing practice.
- End-of-life care – Care and support for patients nearing the end of their life.
- Spiritual care – Providing support and care for a patient’s spiritual and religious needs.
- Complementary therapies – Therapies that are used in addition to traditional medical treatments, such as acupuncture or massage therapy.
- Infection prevention – Preventing the spread of infections in healthcare settings.
- Patient positioning – Positioning patients to promote comfort and prevent complications.
- Patient transfer – Moving patients from one location to another within a healthcare facility.
- Catheterization – Inserting a catheter to drain urine from the bladder.
- Restraint use – Using physical restraints to prevent patient harm or injury.
- Pain medication – Medications used to manage and treat pain.
- Nutritional supplements – Supplements and fortified foods used to meet a patient’s nutritional needs.
- Patient hygiene – Promoting hygiene and cleanliness to prevent infection and promote comfort.
- Fall prevention – Implementing measures to prevent patient falls and injuries.
- Informed consent – Obtaining a patient’s consent for treatment or procedures after providing information on risks and benefits.
- Patient rights – Ensuring patients are aware of their rights and are treated with dignity and respect.
- Skin care – Managing and treating skin conditions and preventing pressure ulcers.
- Medication reconciliation – Ensuring patients receive the correct medications by reconciling medication lists across providers and settings.
- Intraoperative care – Care and management of patients during surgical procedures.
- Post-anesthesia care – Care and monitoring of patients after surgical procedures and anesthesia.
- Respiratory assessment – Assessing a patient’s respiratory status and function.
- Airway management – Maintaining and managing a patient’s airway to promote breathing and oxygenation.
- Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis – Testing and analysis of a patient’s blood to assess respiratory and metabolic status.
- Tracheostomy care – Care and management of a tracheostomy tube used to maintain a patient’s airway.
- Chest tube management – Care and management of a chest tube used to drain fluid or air from the chest.
- Hemodynamic monitoring – Monitoring and assessing a patient’s cardiovascular status and function.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) monitoring – Monitoring a patient’s heart rhythm and function.
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) – Life-saving interventions used to restore breathing and circulation during cardiac arrest.
- Advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) – Advanced interventions used to manage cardiac arrest and other life-threatening emergencies.
- Pediatric advanced life support (PALS) – Advanced interventions used to manage life-threatening emergencies in children.
- Neonatal resuscitation – Life-saving interventions used to restore breathing and circulation in newborns.
- Chest compressions – Manual compressions used during CPR to restore circulation.
- Defibrillation – Electric shock used to restore normal heart rhythm during cardiac arrest.
- Medication titration – Adjusting medication doses based on patient response and assessment.
- Medication side effects – Monitoring and managing side effects of medications.
- Medication interactions – Assessing for potential interactions between medications a patient is taking.
- Patient education – Providing patients with information and resources to help them manage their health and treatment.
- Family education – Providing family members with information and resources to help them support their loved one’s health and treatment.
- Discharge planning – Planning for a patient’s transition from the hospital or healthcare facility to their home or another care setting.
- Case management – Coordinating and managing a patient’s care across different healthcare providers and settings.
- Health promotion – Promoting healthy behaviors and lifestyles to prevent illness and improve health outcomes.
- Wound care – Management and treatment of wounds to promote healing and prevent infection.
- Ostomy care – Management and care of a surgically created opening in the body for the elimination of waste.
- Rehabilitation – Helping patients recover and regain function after an illness, injury, or surgery.
- Patient safety – Ensuring patients are safe from harm or injury during their healthcare experience.
- Quality improvement – Implementing strategies to improve the quality and effectiveness of healthcare services.
- Professional development – Continuing education and development to improve nursing practice and knowledge.
- Telehealth – Providing healthcare services remotely using technology and digital communication.
- Electronic health records (EHR) – Digital records of a patient’s health information and medical history.
- Medication administration – Safe and accurate administration of medications to patients.
- Pain management – Managing and treating pain to promote comfort and quality of life for patients.
- Vital signs monitoring – Regular monitoring and assessment of a patient’s vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature.
- Patient assessment – Comprehensive assessment of a patient’s physical, emotional, and social health to guide care and treatment.
- Medication reconciliation – Ensuring patients receive the correct medications by reconciling medication lists across providers and settings.
- Healthcare informatics – Using technology and data to improve healthcare delivery and outcomes.
- Evidence-based practice – Using current research and evidence to guide nursing practice and decision-making.
- Interprofessional collaboration – Collaborating with healthcare professionals from different disciplines to provide comprehensive and effective care to patients.
-
Supposition Meaning

Once you start talking about things that you are unsure about, sometimes you have to make assumptions. You have to guess at which things are correct and which are not, and come to a conclusion. This is especially true if you are police officer or detective. You need to assume some things are true even […]
-
Summary of how Components of Health are related to Wellness

To truly summarize how the components of health are related to wellness, it’s crucial to understand that well-being is much more than the absence of illness. Interweaving well-being links throughout the various facets of life, the health components and wellness connection present a dynamic framework underpinning a contented and fulfilling existence. Essential to this is […]
-
Understanding the Extroverted Introvert

The social landscape is often painted in binary terms: the outgoing, high-spirited extroverted introverts and their counterparts, the contemplative, reserved introverted extroverts. However, a captivating middle ground exists where certain individuals draw from both wellsprings, interweaving the energies of a shy extrovert with the depth of a social introvert. These are the ambiverts: versatile personalities […]
-
Very vs Vary: Understanding the Difference

When it comes to effective communication in English, it’s crucial to differentiate between words that might sound similar but have distinct meanings. Often, the nuances in language can lead us to confuse synonyms, or in this case, homophones. To distinguish successfully and compare and contrast terms such as ‘very’ and ‘vary’, one must understand the […]
-
Inspiring Introvert Quotes for Quiet Reflection

In a world that often celebrates the loud and the extroverted, there exists a quiet corner where introvert quotes cast a spotlight on the introspective and the contemplative. Each phrase holds a mirror up to the introvert life, illustrating that the roots of creativity and profound thought often stem from the depths of silence. From […]
-
Take a Knee & Run Out the Clock Meaning Explained

In the dynamic world of American football, strategies such as take a knee football and end game tactics often decide the outcomes of tightly-contested matches. Understanding the take a knee and run out the clock meaning is essential for any fan or player who wants to grasp advanced time management in sports and football game […]
-
Understanding “Run Out” Meaning – Quick Guide

Within the rich tapestry of the English language lies the phrasal verb “run out,” a term that is as versatile as it is commonplace. The run out meaning can traverse various scenarios, from the momentary halt in conversation when an argument has been exhausted to the alarming point at which one’s vehicle sputters to a […]
-
What happens when You Run out of Oxygen? Consequences of Oxygen Deprivation

The idea of running out of breath is a universal fear, but do you know what actually unfolds within your body when it’s starved of oxygen? Beyond the gasp for air and the inevitable panic, the symptoms of oxygen depletion trigger a cascade of potentially lethal physiological events. Most of us are aware that oxygen […]
-
Frases de Cumpleaños Únicas para Celebrar | Mensages

Encontrar las palabras exactas para desear ‘feliz cumpleaños’ a un ser querido puede ser todo un arte. ¿Sabías que las frases de cumpleaños tienen el poder de convertir un mensaje en un regalo para el alma? En esta era digital, donde los mensajes de cumpleaños a menudo se comparten con un clic, destacar con felicidades […]
-
What is the differences between Cattle and Livestock?

‘Cattle’ is only used when talking about cows and bulls kept on a farm for milk or meat. ‘Livestock’ refers to all the animals that are kept on a farm for use and profit. For example, sheep, pigs, horses, and, of course, cows. Did you lose many cattle to wolves? There’s a fantastic market for […]
-
Explore the Variety of Ecosystems on Earth

Planet Earth hosts an immense tapestry of life, a testament to ecosystem diversity that pervades every corner of the globe. From the lush depths of ancient rainforests to the enigmatic expanse of desert landscapes, our world comprises diverse ecosystem categories that sustain the complex web of life. Diving into the myriad forms that nature takes […]
-
Master Connectors en Español: Mejora tu Escritura

¡Bienvenido! En este artículo, te enseñaremos cómo mejorar tu escritura en español utilizando conectores. Los conectores son palabras o frases que te permiten conectar ideas y darle coherencia a tus textos. Si deseas expresarte de manera clara y fluida en español, los conectores son herramientas fundamentales que debes dominar. Estas palabras te ayudarán a establecer […]
-
Get Marble in LEGO Fortnite – Quick Guide!

Welcome to our quick guide on how to get marble in LEGO Fortnite. If you’re a fan of the game, you know that marbles are valuable items that can enhance your gaming experience. Whether you’re looking to complete collections or unlock special features, marbles are essential. In this guide, we’ll show you how to find […]
-
Miracle Morning Book: Transform Your Life

Are you tired of waking up feeling groggy and unproductive? Do you wish you had more time in the day to focus on your goals and personal development? Implementing the practices mentioned in the “Miracle Morning” book can have a profound impact on your life. Many readers have reported increased focus, motivation, and a greater […]
-
Which Water Source May Become Polluted as It Travels Over Land?

Throughout the United States, waterways are vital lifelines. However, with the continuous interaction between land and water, polluted water sources are unfortunately commonplace, posing serious risks to ecosystems and human health. A primary cause for alarm comes from the widespread issue of water pollution over land, where water travel itself becomes a conduit for introducing […]
-
Explore the Mysteries in “Book of Clarence” Now

Welcome to the enchanting world of “Book of Clarence”! Prepare to embark on a journey that will captivate your imagination and touch your heart. This mesmerizing tale of resilience and discovery will leave you craving for more. Unveiling the profound depths of Clarence’s story, this book takes you on an awe-inspiring adventure of self-discovery and […]
-
Unpack Gonna Gotta Wanna Outta Kinda Meaning
Ever found yourself puzzled by the rapid-fire slang that zips through casual American conversations? You’re not alone. The world of American English is often peppered with contractions like gonna, gotta, wanna, outta, and kinda, each holding a special spot in the lexicon of colloquial communication. These phrases might seem elusive at first, but their ubiquity […]
-
What is the difference between Weather and Climate?
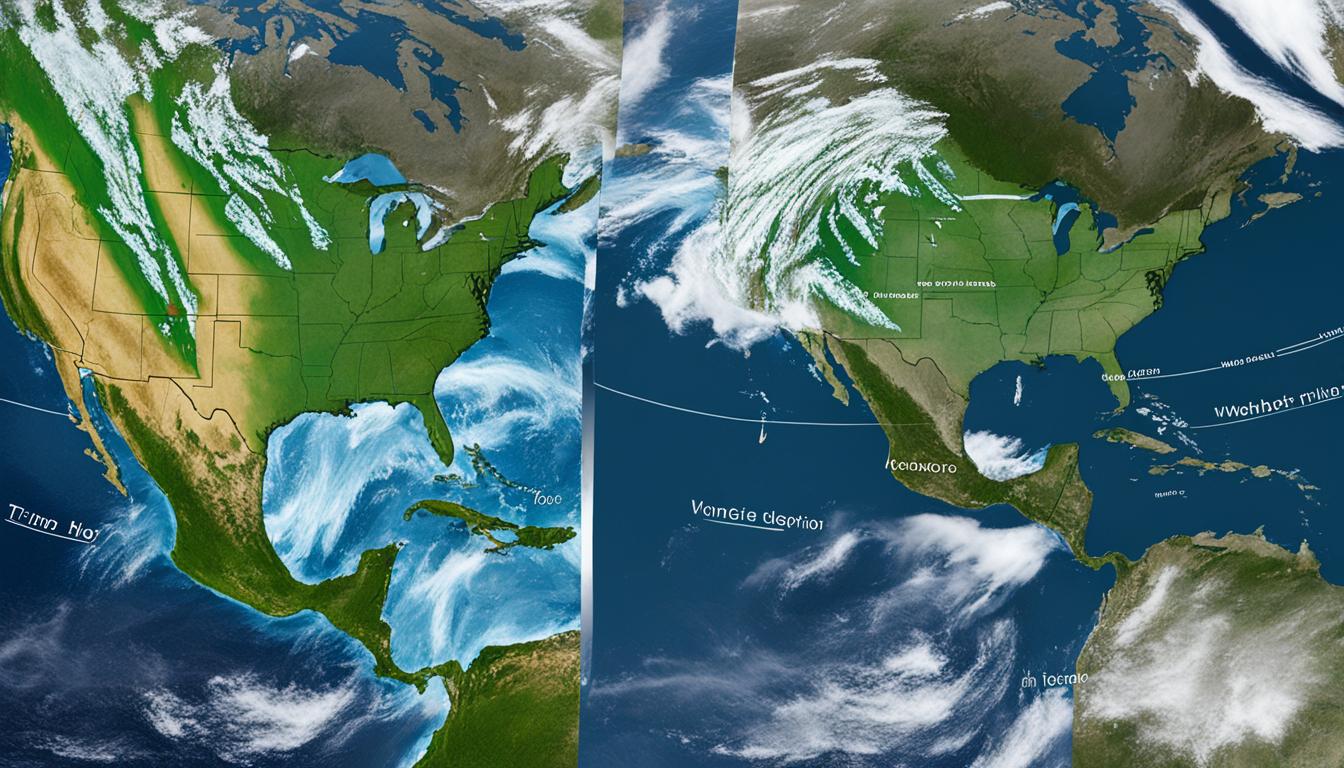
Have you ever wondered about the difference between weather and climate? When you think of weather, you’re thinking of what your outfit will be for the day. The weather defines a mix of events that occur in our atmosphere on any given day – like when it rains you grab an umbrella, or when it’s […]
-
How an Environmental Change Can Lead to the Development of a New Species?

As a nature enthusiast and a fervent advocate for the wonders of evolution, I’ve always been intrigued by the evolutionary consequences of environmental changes. There’s something truly fascinating about witnessing the power of nature as it nudges organisms along the path of ecological adaptation and speciation. It reminds me that we’re part of a dynamic, […]
-
Understanding CFCs and Smog Pollution Types
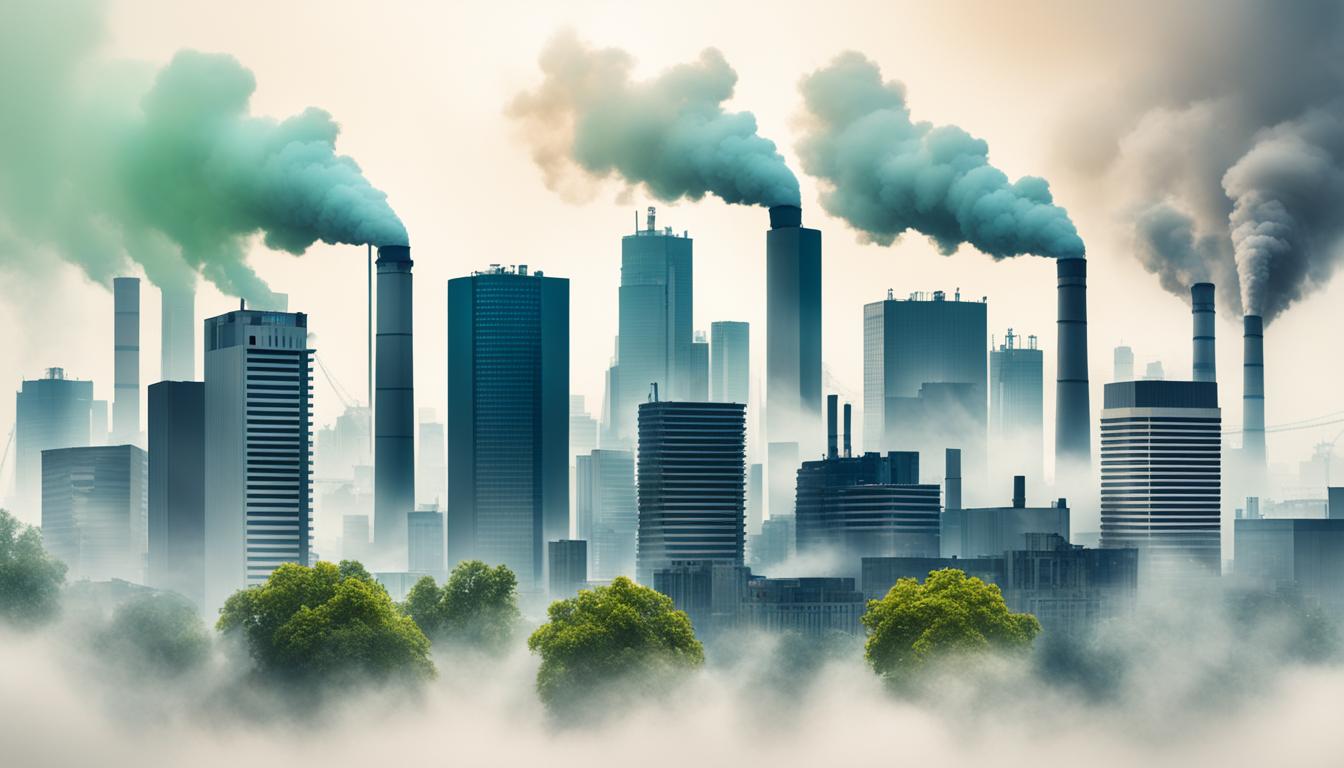

If you’ve ever looked up at a hazy sky and wondered about the quality of the air you’re breathing, you’re not alone. Air pollution, an unfortunate byproduct of modern progress, ranks as one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time. From rural landscapes to bustling cities, the causes of pollution are widespread, igniting […]
-
How can I get my students to talk to me more during class?

Engaging students in classroom discussions is a vital component of fostering a positive learning environment and promoting active learning. However, it can sometimes be challenging to encourage all students to actively participate and share their thoughts. In this article, I will answer the question: “How can I get my students to talk to me more […]
-
Are there platforms where I can pay someone to talk to me in a different language for practice?

If you’re looking to improve your language skills through conversation practice, there are several platforms available where you can pay someone to talk to you in a different language. These platforms provide opportunities to engage in real conversations with native speakers, helping you develop fluency and confidence. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced learner, […]
-
इंग्लिश वाक्य में योजना कैसे करें?

यह इकाई छात्रों को इंग्लिश भाषा में योजना बनाने की कला सीखने के बारे में बताएगी। योजना का मतलब होता है किसी कार्य को ध्यानपूर्वक तैयार करना। यहां छात्रों को इंग्लिश वाक्य में योजना कैसे बनाएं इस प्रश्न का उत्तर दिया जाएगा। मुख्य बातें: इंग्लिश वाक्य में योजना का महत्व। इंग्लिश वाक्य में योजना बनाने […]
-
मेरे सुझाव: आसान अंग्रेजी व्याकरण सीखें

नमस्ते! मैं आपके लिए एक सुझाव लेकर आया हूँ जो आपकी मदद करेगा अंग्रेजी व्याकरण को आसानी से सीखने में। इस आर्टिकल में हम अंग्रेजी व्याकरण के नियम, एंग्लिश व्याकरण का महत्व, और अंग्रेजी व्याकरण को सीखने के आसान तरीके के बारे में बात करेंगे। मुख्य बातें: अंग्रेजी व्याकरण के नियमों की समझ अंग्रेजी भाषा […]
-
मेरे अनुभव से व्याकरण सीखने की सरल गाइड

व्याकरण हिंदी भाषा को शुद्ध रूप में लिखने और बोलने के नियमों का विषय है। इसमें हम वर्णों, मात्राओं, संज्ञाओं, विशेषणों, संख्याओं, क्रियाएँ, सर्वनाम, लिंग और वचन के बारे में सीखते हैं। हिंदी व्याकरण का अध्ययन हमें भाषा के नियमों का समझने में सहायता करता है और हमें सही तरीके से वाक्य रचना और संज्ञाओं […]
-
क्रिया और सकर्मक क्रिया के बीच के अंतर समझें

क्रिया और सकर्मक क्रिया में अंतर की समझ के लिए हमें दोनों के बारे में विस्तृत जानकारी हासिल करनी चाहिए। क्रिया एक कार्य या क्रियान्वित करण को दर्शाती है, जबकि सकर्मक क्रिया में कार्य को कर्ता द्वारा किया जाता है और कर्म को प्रभावित किया जाता है। इसमें भाषा प्रसंग, वचन, लिंग, समय, पुरुष, वाच्य, […]
-
Explore the Unforgettable Jungle Book Vultures with Me

The Jungle Book is a beloved Disney film that has captured the hearts of audiences for generations. One of the iconic characters from the film is the Jungle Book vultures. These quirky characters play a significant role in the story and have become fan favorites. Join me as we dive into the world of the […]
-
Meet the Jungle Book Panther named Bagheera: Fierce, Wise, and Endearing

Hey there, fellow Jungle Book enthusiasts! Today, I’m thrilled to introduce you to the magnificent character who has captured the hearts of audiences worldwide – the Jungle Book Panther. As Mowgli’s panther friend, this black panther character goes by the name of Bagheera. Bagheera is more than just a fierce and powerful predator. With his […]
-
Your Guide: List of 30 Helpful Synonyms with Explanation and Examples

Welcome to my comprehensive guide on helpful synonyms! In this article, I will provide you with a list of 30 helpful synonyms, along with detailed explanations and examples. If you’re looking to enrich your vocabulary and improve your English language skills, you’ve come to the right place. Having a wide range of synonyms at your […]
-
Complex Sentences and Compound Complex Sentences in English

Hello, fellow writers and language enthusiasts! Today, I want to delve into the fascinating world of complex sentences and compound sentences in the English language. These two concepts play a vital role in sentence structure and types, and understanding them can greatly enhance your writing skills. So, let’s explore the characteristics of complex and compound […]